opalindustries.us
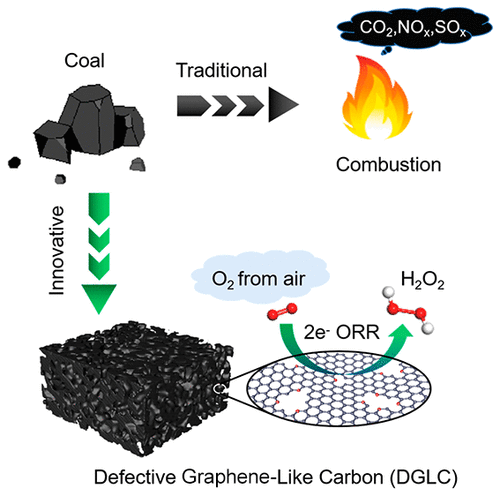
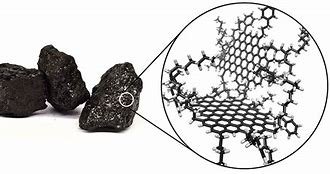
Converting Coal to Graphene
Converting coal to graphene is an intriguing process with potential applications in materials science and technology. Here are a couple of methods:
Graphene from Coal via Nitric Acid:
- Researchers have found a way to create graphene from coal using nitric acid. Here’s how it works:
- Ground and purified coal is immersed in a bath of nitric acid.
- The acid converts the coal into graphene oxide.
- After draining off the acid, any unreacted carbon is removed, leaving behind graphene oxide powder.
- This graphene oxide powder can then be further converted to graphene through heat treatment1.
- Researchers have found a way to create graphene from coal using nitric acid. Here’s how it works:
Computer Simulations for Coal-to-Graphite Conversion:
- Scientists at Ohio University used computer simulations to explore the conversion of coal to graphite.
- They created a simplified “coal” consisting of only carbon atoms.
- By subjecting this simplified coal to high pressure (around 3,000 Kelvin or nearly 5,000 Fahrenheit) and studying its behavior, they gained insights into the conversion process.
- While the sheets did form, the carbon atoms didn’t always develop simple six-carbon rings; some rings had five or seven carbons.
- These findings contribute to our understanding of coal-to-graphite transformation2.
In summary, both experimental and computational approaches are shedding light on the fascinating world of coal-to-graphene conversion